Table Of Contents:
- How to Set Up Business Email
- Key Takeaways
- Why you need business email addresses
- What you need to get started with business email
- Should you register your domain with the same people that host your emails?
- Creating a business email address
- Configuring your devices
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
How to Set Up Business Email
This article explains how to set up business email addresses with ease. It covers why business email addresses matter and what you need to get started. The guide also examines the option of registering your domain with the same service for email and explains how to create a business email address and configure your devices to gain the functionality you require and also tacking data storage in to account.
Key Takeaways
- business email addresses build trust and a consistent professional brand image
- secure mail configuration ensures reliable communications that can’t be intercepted
- integrated domain and email hosting simplifies management and support procedures
- pop and imap offer distinct approaches with benefits and limitations for email management
- considering where your emails are stored is key to business continuity
Why you need business email addresses
Business email addresses promote trust in communications and reinforce brand identity. Using an email address that has your own unique, business specific domain after the @ sign, promotes a sense of trust in the clients and customers that you communicate with.
Legitimacy and trust for business communications
Businesses benefit from using business email addresses as they create a professional brand image and build user trust when communicating with clients. It’s important to register a domain to ensure these email address and your website are properly associated. Using a free email service that results in you using an @gmail.com or an @hotmail.com address doesn’t tend to foster such a degree of trust or legitimacy. This is because anybody can create free @gmail.com or @hotmail.com email addresses.
Registering your own domain then using it to operate mail services and your website gives a sense of credibility, trust, and that you business has been invested in. Using a free email service tends to give the impression of a half hearted, or make do approach to your business, which doesn’t tend to imply credibility or build trust. Often, using a free email address will put a potential customer off from the offset, and some potential customers won’t entertain using businesses to provide services if they rely on free email addresses.
Brand Identity
Establishing a business email address by register a domain promotes an identifiable brand image by ensuring that every communication is routed through the same domain as the one used by your website. By using your own unique business specific domain for both your email addresses and your website you create a unified identity. What this means in real world terms is that you can let your colleagues communicate with a customer you’ve previously been dealing with, and because both email addresses have the same domain after the @ sign, both you and your colleague appear associated from the perspective of your customer.
What you need to get started with business email
This section covers the essentials for business email setup, including domain registration and a hosting account. Unlimited hosting is good for IMAP, cheaper hosting with disk space limtis can be used for POP3. More about the difference between POP3 and IMAP is covered later in this article. To keep things simple for now:
- IMAP is what you’ll need if you want more than one device (i.e. a phone and a laptop) connected to a mailbox and you’d like email to appear consistent across both. IMAP emails are also backed up when using a mailbox hosted with netnerd.com.
- POP3 is fine to use if you only use one device to collect emails, provided this device is backed up (as the collected emails exist on the device alone).
Domain registration
The domain is the part of the email address after the @ sign. The domain is also the address of your website after the www’s. As well as a domain being part of your brand identity, domains are also key to where traffic routes, or in this case, where emails arrive.
When registering a domain it’s worth choosing a domain that suits your business and also that’s SEO friendly.
Hosting account
The hosting account is where your mailboxes, and most likely your emails (unless you’re collecting using POP3) are stored. Using unlimited hosting is good for IMAP email collection. This is because when you use IMAP emails are stored in your hosting account. If you use a hosting account with a disk space limit, if the limit is reached, you’ll stop receiving emails. If you use POP3 to collect your emails, emails are downloaded, so they aren’t stored in the hosting account. While this can save on cost by using a cheap hosting account with a disk space limit, it does also mean that emails can’t be backed up by your hosting provider, and also that emails won’t be consistent if you connect more than one device to your mailbox.
The easiest way to think about the POP3 or IMAP situation is that if you’d like your mailbox to look the same on all devices (with regard to read, unread, sent and replied to emails) you need to use IMAP.
Should you register your domain with the same people that host your emails?
There are some people that say you should do this, and there are some people that say you shouldn’t do this. There are benefits and downsides to both. If you’d like just one party to deal with for both cost and technical support, then registering your domain with the same party is most likely the best course of action to take.
Ease of use
Registering a domain with the same provider that hosts emails means that a lot can be done for you. Your billing is unified with one party, so you them to renew your email related services as a whole. operating in this manner also means you have one party involved with the administration of your email services as a whole. Using your mail providers nameservers means that a lot of default configuration is in place automatically, which can help with email deliverability (the chance of people receiving your emails). If you don’t use your email providers nameservers, this puts you in the position where you’ll have to administer the email aspect of your domain’s DNS, which isn’t to everyone’s liking.
DNS not being configured correctly for your domain can result in:
- Your emails not being received by recipients.
- You not receiving emails that you’ve been sent.
- Emails you send being directed to junk or spam folders.
One party to liaise with for support
Using one provider for both business email hosting and domain registration simplifies support queries and troubleshooting. If you do have problems with your email service and you’re using one party for your domain and emails, you only have to speak to one provider to gain assistance, or to have problems addressed. If you use a different party for your domain and your email service, this can put you in the position where you have to pass information between two parties, or have to apply fixes yourself.
Companies that select a single provider for business email and domain registration benefit from a streamlined support process that reduces downtime and enhances productivity. This strategy not only sustains business operations but also bolsters client confidence by ensuring reliable, secure communications that underpin effective marketing initiatives.
Creating a business email address
This section explains setting up a mailbox in cPanel and obtaining device settings for a professional setup.
Creating the mailbox in your cPanel
Creating the mailbox in cPanel is fairly straight forward. Initially you’d log in to your cPanel, then click on “Email accounts”:
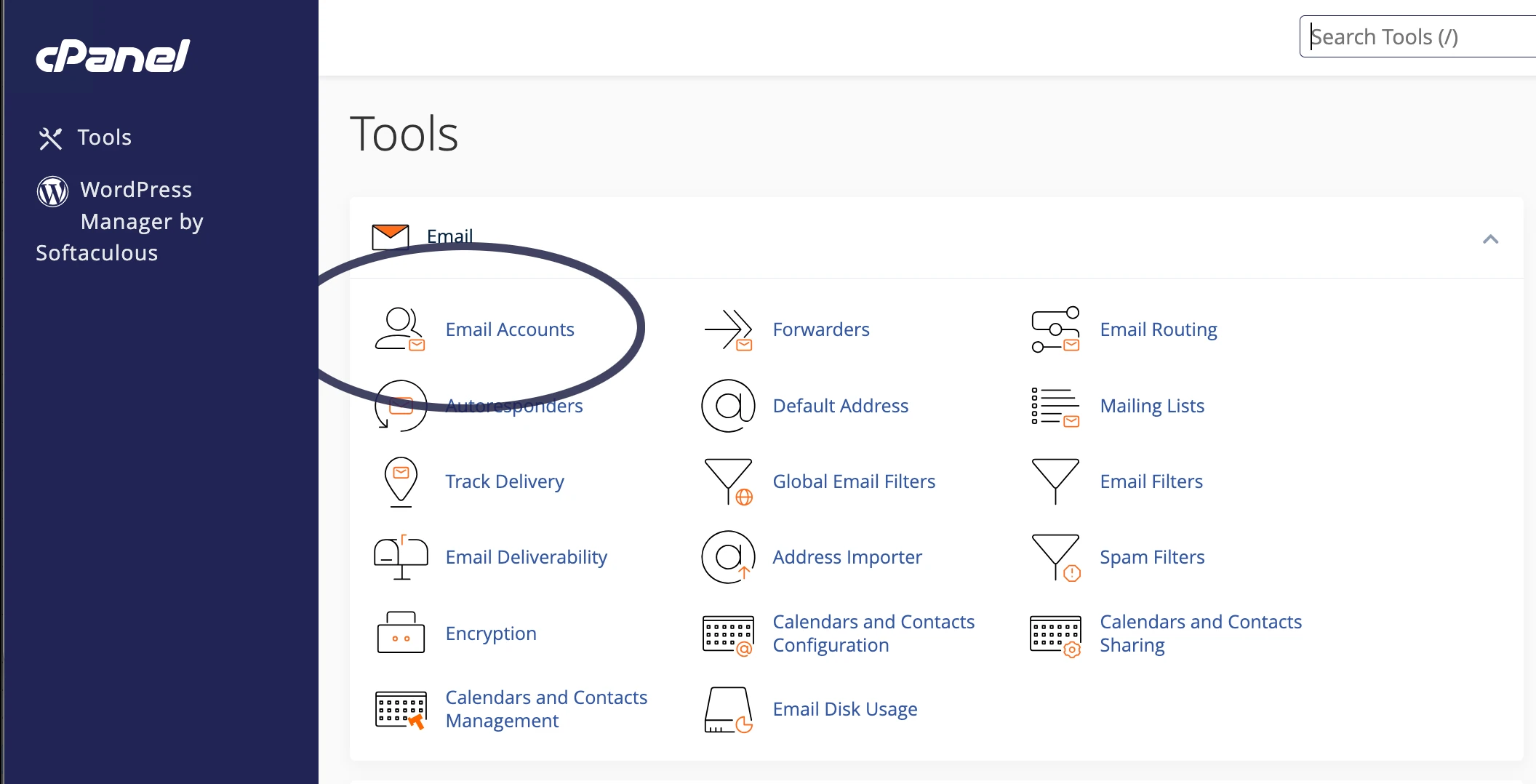
You’d then click the “create” button on the right hand side:
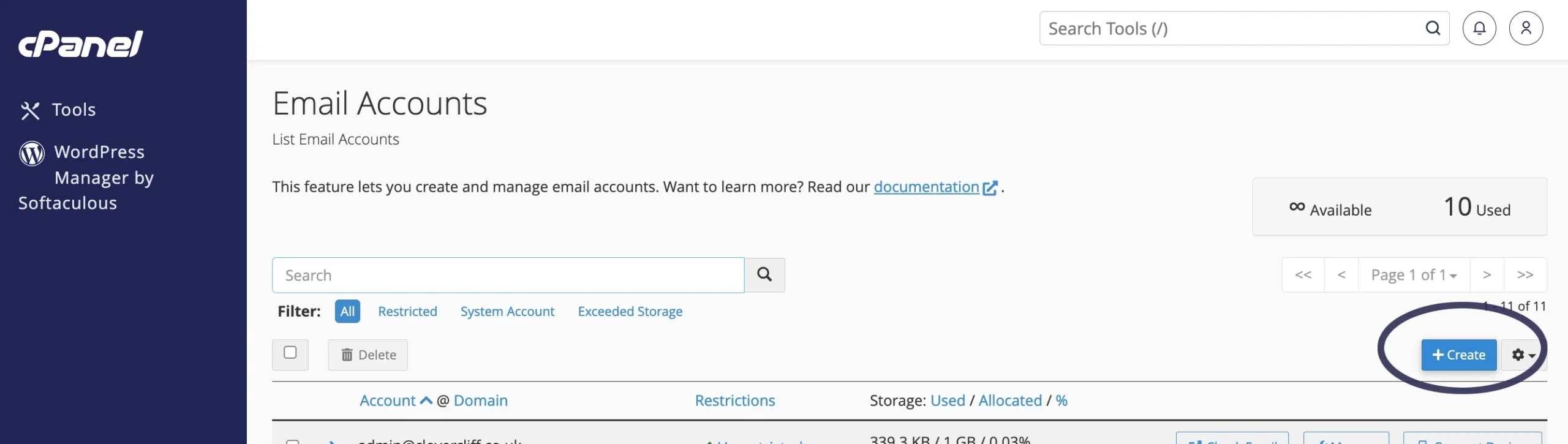
You then enter the part of the email address that you’d like before the @ sign in the “username’ field, enter the password you’d like to use for your email address and MAKE A NOTE OF THE PASSWORD as you can’t view this in retrospect. Then click the “create” button.
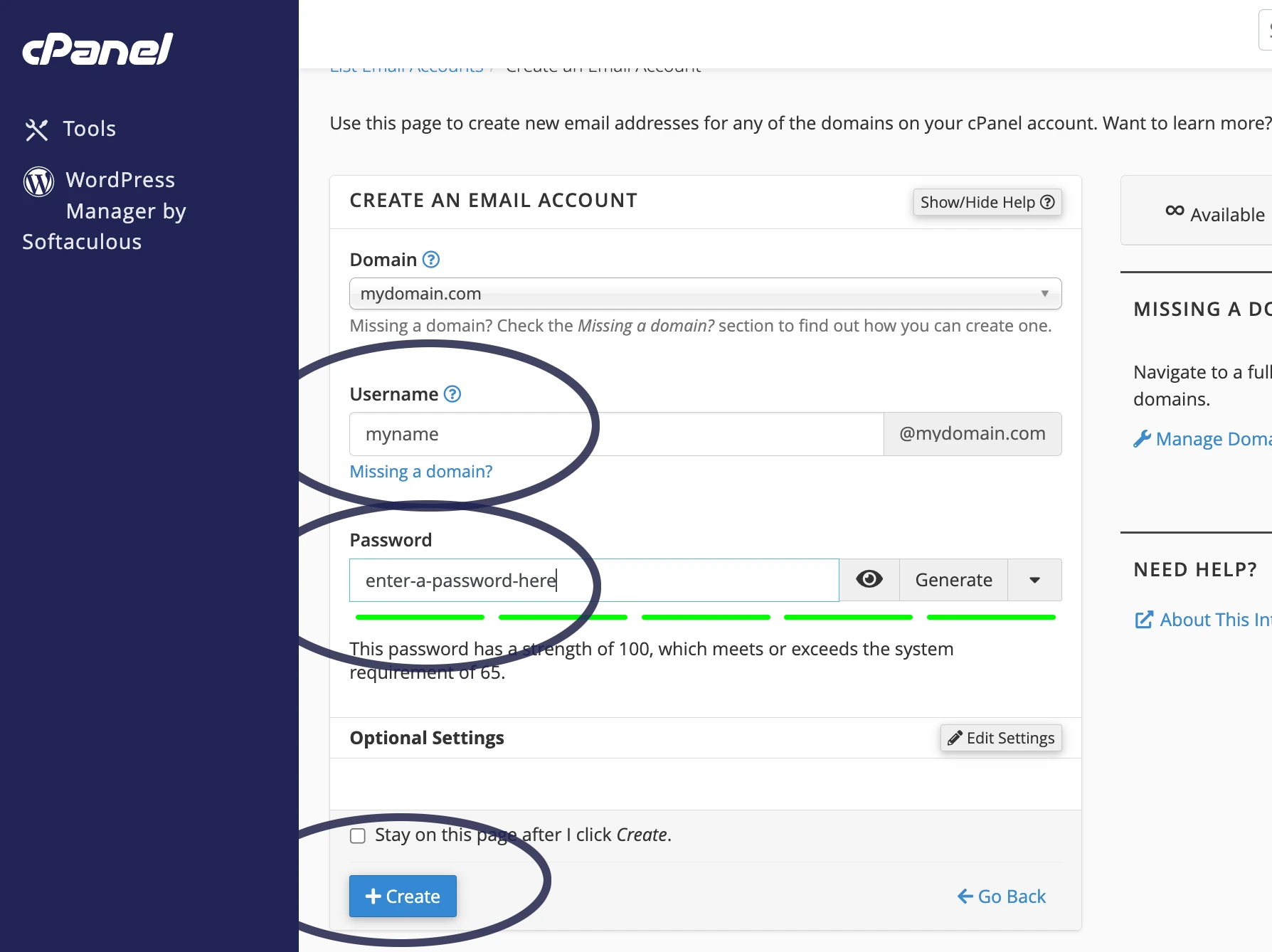
Once the mailbox has been created you’ll then be returned to the “email accounts” page.
Obtaining device settings
To obtain the settings that you’d need to enter in to a mail client/program such as Outlook, Thunderbird or the mail program on your phone, click on the Email Accounts icon:

And then click on the “connect devices” button:
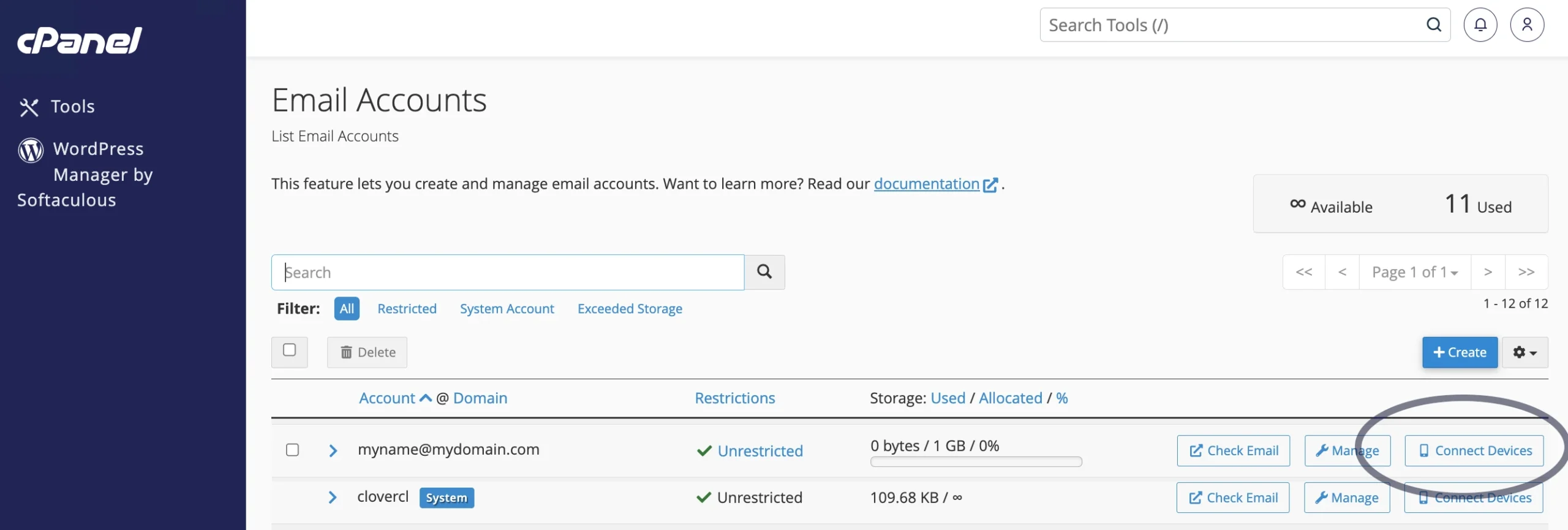
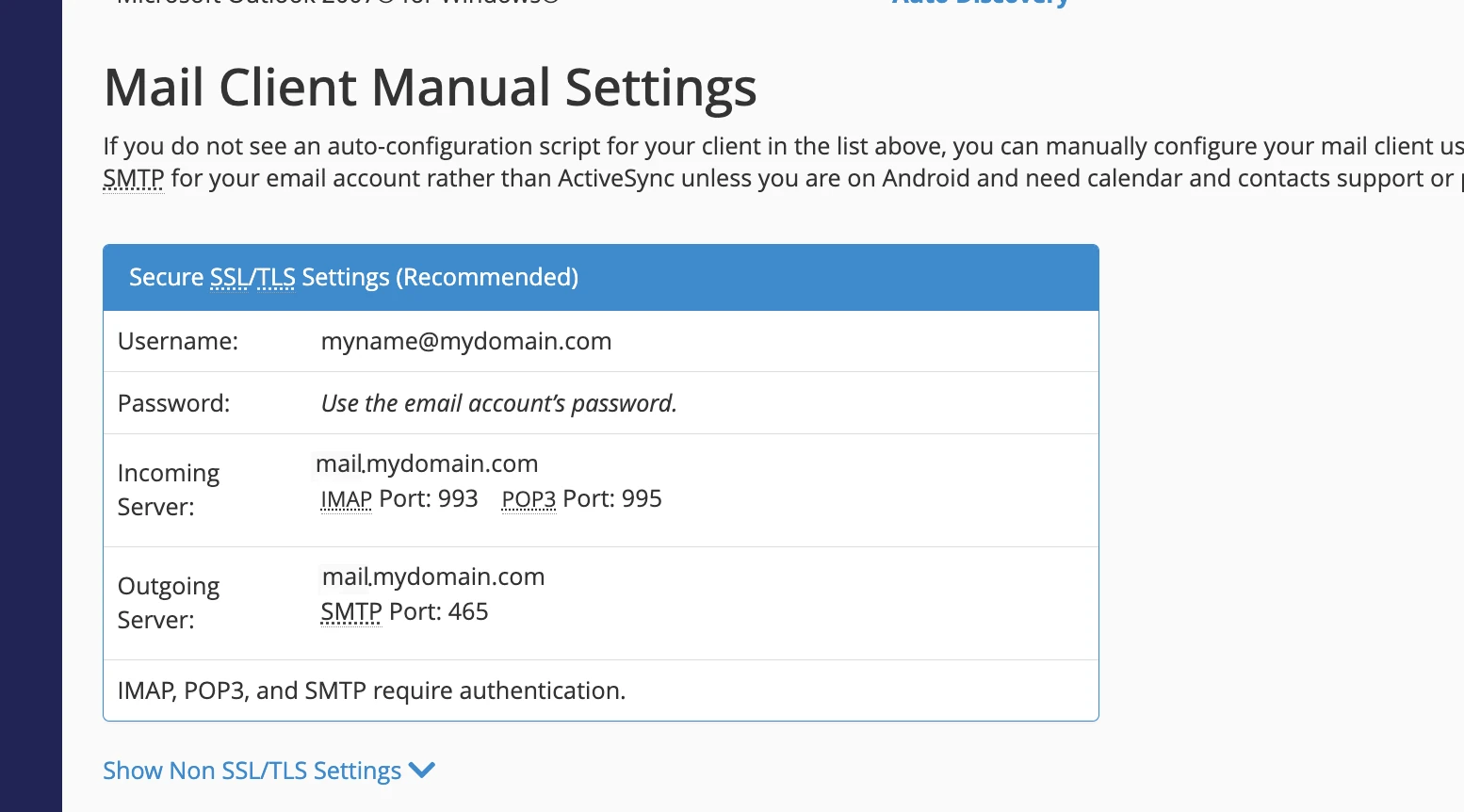
And you’ll then be presented with the settings you’d need to enter into a device to be able to send and receive emails:
Administrators utilise comprehensive software tools to verify that every device setting aligns with their customer’s security needs, thus reinforcing reliable business communication. The setup process includes checking network details and encryption standards to assure robust performance and secure access at all times.
Configuring your devices
This section covers configuring devices to collect and send emails.
Generally speaking, you should always configure your devices to use encryption when sending or receiving emails. This usually involve selecting SSL or TLS in your mail client and using the respective ports:
- Encrypted IMAP: 993
- Encrypted POP3: 995
- Encrypted SMTP: 465
The reason it’s always a good idea to use encryption is because this prevents data being intercepted in transmission between the mail server and the device. This prevents passwords and usernames being obtained along with email data. If you ever use any kind of open Wifi network (in restaurants, hotels, pubs or cafes) encryption is a must have.
But what’s all this POP3, IMAP and SMTP business?
The difference between POP3, IMAP and SMTP.
POP3 and IMAP are both used to collect emails. SMTP is used to send emails.
Although POP3 and IMAP are both used to collect or access emails you’ve been sent they both function in different ways.
POP3 downloads emails to the device you’re using (your phone or laptop for example). If your mailbox on the server is accessed using POP3, any emails held in the mailbox are downloaded to the device used to access the mailbox. The emails then exist on that device (not on the mailbox on the server). If a second device then tries to collect emails, there aren’t any to collect, as they’ve already been collected and downloaded to the first device.
Because emails collected using POP3 no longer exist on the server, your email provider can’t back these up. You’d have to back up the device you’re using to collect emails for POP3 emails to be backed up. If you’re collecting using POP3, and you need emails restoring, your mail provider can’t do this for you, because the emails don’t exist on their platform.
IMAP is a synchronisation rather than a collection. When you collect emails using IMAP, you’re not really collecting as such. What you’re doing is synchronising email data between a mailbox held server side and a device. If you mark an email as read on a device, the email is marked as read in the mailbox on the server. If you delete an email on a device, it’s deleted on the server. If you create a mail folder on a device, it’s created on the server. If you move an email in to the folder, this move also takes place in the mailbox on the server.
When using IMAP, all mail actions taken on a device are sync’d to the mailbox on the server.
As all devices all connect to the mailbox on the server (there’s no device to device communication), they all see emails and mailboxes in the same state.
IMAP is good to use if you’d like your mailbox and it’s content to appear the same on all the devices you use to collect emails.
IMAP does mean that all mail is stored in a mailbox on the server, which can result in using greater amounts of disk space particularly if:
- You’ve used your mailbox for long periods of time
- You send or receive (or both) large volumes of emails
- You send or receive emails with large attachments
IMAP offers greater flexibility for users requiring access across multiple devices, contrasted with POP’s one-off download method that may restrict functionality. This distinction is critical for businesses aiming to optimise communication protocols and system performance, as shown in the following table:
Advantages of POP3 collection
POP3 collection offers a straightforward approach with a simple collect and download. As emails aren’t held server side, very little (or no) disk space is used server side by storing emails, which means you can use a cheaper hosting package with a disk space limit:
Disadvantages of POP3 collection
POP3 collection isn’t a good idea if you collect emails on multiple devices. This is because emails that have been collected by device A won’t be available on device B if device A has already downloaded them.
POP3 collected emails are also stored on your device, so if your device breaks, your emails could be lost. Backing up emails stored on your device are also your responsibility so you’ll need to know how to do this.
Advantages of IMAP
IMAP provides reliable synchronisation across devices, ensuring that mailbox content remains consistent and accessible on every device. Using IMAP results in messages being stored on the server, which means your mail provider can backup and restore emails for you:
Disadvantages of IMAP
The main disadvantage of IMAP is specific to the space used to store emails server side. This can result in the need to use a more expensive hosting account. If you’re using a hosting account with a disk space limit and are using IMAP to access emails, this can result in your account’s disk space being reached. If this happens, you won’t receive emails.
IMAP can be a bit harder for some people to understand. For example, if you delete an email from an IMAP configured device, the instruction to delete is sent to the mailbox held server side. This deletes the mail. Any devices that then sync with the mailbox no longer have access to the deleted email.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of a business email address?
A business email address boosts brand credibility, strengthens customer trust, and simplifies communication management while reinforcing a consistent professional image that supports business growth.
What do you need to start business email hosting?
Begin by securing a domain and reliable web hosting plan, then configure your email server settings and security features. Netnerd offers quality, affordable web hosting with unlimited disk space, domain registrations, reseller hosting and managed VPS for seamless business email hosting.
Should domain registration and email hosting be combined?
Integrating domain registration with email hosting streamlines management/support and reduces costs; Netnerd provides reliable, combined solutions that suit business owners and small businesses seeking efficient web hosting and domain services.
How does one create a business email address?
Creating a business email address requires registering your domain, setting up hosting with a trusted provider, and configuring email accounts via your hosting control panel; providers like Netnerd offer reliable, affordable solutions tailored for business email needs.
How can devices be configured for business email?
Devices can be configured by accessing email settings, entering server information, and authenticating with business credentials. IT support is recommended for verifying the settings and ensuring secure email performance on each device.
Conclusion
Setting up a business email system is a fundamental step for establishing a professional brand image and ensuring secure communication. It establishes legitimacy by reducing risks associated with phishing and spam while providing a well-organised, efficient workflow. The process involves selecting a robust domain registrar and hosting service, as well as configuring devices for optimal performance. This practical approach improves customer interactions and supports sustained business growth.